本文檔介紹對ACI中的間歇性丟棄進行故障排除的步驟。
This document describes the steps taken to deactivate intermittent disposal in ACI.
本文中的資料摘自疑難排解思科以應用程式為中心的基礎架構第二版書籍,尤其是交換矩陣內轉送 — 間歇性丟棄一章。
The data in this paper are taken from Systemsco uses application as a centrality for the second edition of the prototype book, especially for
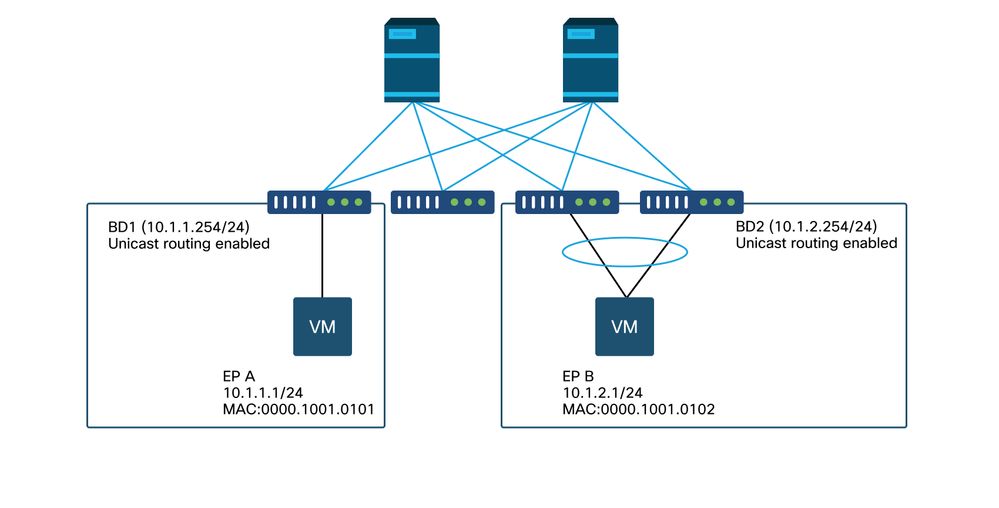
在本例中,從EP A(10.1.1.1)到EP B(10.1.2.1)的ping遇到間歇性下降。
In this case, there was an intermittent decline in ping from EP A (10.1.1.1) to EP B (10.1.2.1).
[EP-A ~]$ ping 10.1.2.1 -c 10
PING 10.1.2.1 (10.1.2.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=231 time=142 ms
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=231 time=141 ms
<-- missing icmp_seq=3
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=231 time=141 ms
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=231 time=141 ms
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=231 time=141 ms
<-- missing icmp_seq=7
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=8 ttl=231 time=176 ms
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=9 ttl=231 time=141 ms
64 bytes from 10.1.2.1: icmp_seq=10 ttl=231 time=141 ms
--- 10.1.2.1 ping statistics ---
10 packets transmitted, 8 received, 20% packet loss, time 9012ms
1.確定導致間歇性跌落的方向
在目的主機(EP B)上執行資料包捕獲(tcpdump、Wireshark等)。 對於ICMP,請關注序列號,以檢視在EP B上觀察到的間歇性丟棄的資料包。
In the case of ICMP, note the serial number to view the intermittently discarded packages observed on EPB.
[admin@EP-B ~]$ tcpdump -ni eth0 icmp
11:32:26.540957 IP 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.1: ICMP echo request, id 3569, seq 1, length 64
11:32:26.681981 IP 10.1.2.1 > 10.1.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 3569, seq 1, length 64
11:32:27.542175 IP 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.1: ICMP echo request, id 3569, seq 2, length 64
11:32:27.683078 IP 10.1.2.1 > 10.1.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 3569, seq 2, length 64
11:32:28.543173 IP 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.1: ICMP echo request, id 3569, seq 3, length 64 <---
11:32:28.683851 IP 10.1.2.1 > 10.1.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 3569, seq 3, length 64 <---
11:32:29.544931 IP 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.1: ICMP echo request, id 3569, seq 4, length 64
11:32:29.685783 IP 10.1.2.1 > 10.1.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 3569, seq 4, length 64
11:32:30.546860 IP 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.1: ICMP echo request, id 3569, seq 5, length 64
...
- 模式1 — 在EP B資料包捕獲時觀察到所有資料包。
丟棄應位於ICMP回應回覆(EP B到EP A)中。
Discarded in ICMP response (EPB to EPA).
- 模式2 — 在EP B資料包捕獲中觀察到間歇性丟包。
丟棄應在ICMP回應中(EP A到EP B)。
Discard in ICMP response (EPA to EP B).
2.檢查具有相同源/目標IP的另一個協定是否具有同樣的問題
如果可能,請嘗試使用兩個端點之間協定允許的不同通訊協定(例如ssh、telnet、http、..)測試兩個端點之間的連線。
If possible, try using the different communication protocols (e.g. ssh, telnet, http,.) that are agreed upon between the two endpoints to test the connection between the two endpoints.
- 模式1 — 其它協定具有相同的間歇性丟棄。
問題可能出現在終端擺動或隊列/緩衝中,如下所示。
Problems may arise in end-of-life swings or queues/buffers, as described below.
- 模式2 — 只有ICMP具有間歇性下降。
轉送表(例如終端表)應該沒有問題,因為轉送是基於MAC和IP的。佇列/緩衝也不能作為原因,因為這會影響其他通訊協定。ACI基於協定做出不同轉發決策的唯一原因是PBR使用情形。
Transfer forms (e.g. terminal) should have no problem, because they are based on MAC and IP. Nor should they be listed/plugged for reasons that affect other communications agreements. The only reason ACI agreed to make different decisions is because PBR is used.
一個可能性是其中一個脊柱節點出現問題。當通訊協定不同時,來源和目的地相同的封包可能會被輸入枝葉負載均衡到另一個上行鏈路/光纖連線埠(即另一個主幹)。
One possibility is that there is a problem with one of the spinal nodes. When communication protocols are different, the same package from the source and destination may be entered into a branch load equal to another upper link/light link port (i.e. another backbone).
原子計數器可用於確保不會在脊柱節點上丟棄資料包並到達出口枝葉。如果封包沒有到達輸出枝葉,請檢查輸入枝葉上的ELAM以檢視封包傳送出去的光纖連線埠。要將問題隔離到特定的主幹,可以關閉枝葉上行鏈路,強制流量流向另一個主幹。
Atom counters can be used to ensure that the package is not discarded on the spinal nodes and that it reaches the export branch. If the package does not reach the end of the branch, check the light link port sent out by ELAM on the branch as a view of the package. To separate the problem to a specific cause, the branch can be shut down and the flow made to another main cause.
3.檢查它是否與終端學習問題相關
ACI使用終端表將資料包從一個終端轉發到另一個終端。間歇性可達性問題可能由端點抖動引起,因為不適當的端點資訊會導致將資料包傳送到錯誤的目的地或將資料包合約丟棄,因為資料包被分類為錯誤的EPG。即使目標應該是L3Out而不是終端組,也要確保IP未獲知為任何枝葉交換機上同一VRF中的終端。
ACI uses a terminal form to transfer the package from one end to another. Intermittent accessibility problems may be caused by peer shaking, because inappropriate peer information can lead to the transfer of the package to the wrong destination or the abandonment of the package because the package is classified as an EPG. Even if the target should be L3Out rather than the end group, make sure that IP is not known as the end end of the same VRF on any branch switch.
請參見本部分的「端點抖動」子部分,瞭解有關如何對端點抖動進行故障排除的更多詳細資訊。
Read more detailed information about how to fail to remove peer shaking in the sub-section of this section.
4.通過更改流量頻率檢查它是否與緩衝問題相關
增大或減小ping間隔,檢視丟棄率是否發生變化。間隔差應足夠大。
Increases or reduces the ping interval to see if the discard rate has changed. The distance should be large enough.
在Linux中,「 — i」選項可用於更改時間間隔(秒):
In Linux, the '-i'option can be used to change the time interval (seconds):
[EP-A ~]$ ping 10.1.2.1 -c 10 -i 5 -- Increase it to 5 sec
[EP-A ~]$ ping 10.1.2.1 -c 10 -i 0.2 -- Decrease it to 0.2 msec
如果丟棄率在間隔縮短時增加,則可能與終端或交換機上的排隊或緩衝有關。
If the discard rate increases at short intervals, it may be associated with queues or buffers on end or switchboards.
要考慮的丟棄比率為(丟棄數/傳送的資料包總數)而不是(丟棄數/時間)。
The disposal rate to be considered is the sum of the data packages (discards/distributions) rather than (discards/times).
在這種情況下,請檢查以下內容。
In this case, please check the following.
- 檢查交換器介面上的任何捨棄計數器是否隨著ping的增加而增加。有關詳細資訊,請參閱「交換矩陣內轉發」一章中的「介面丟棄」部分。
- 檢查Rx計數器是否隨目標終結點上的資料包一起增加。如果Rx計數器的增加值與傳輸的資料包的數量相同,則資料包很可能在端點本身被丟棄。這可能是由於TCP/IP堆疊上的終端緩衝。
例如,如果100000以儘可能短的時間間隔傳送ping,則可觀察到端點上的Rx計數器按秒遞增100000。
For example, if 100,000 transmits ping in as short a time as possible, the Rx counter on the endpoint is observed to increase by 100,000 per second.
[EP-B ~]$ ifconfig eth0
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.1.2.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.1.2.255
ether 00:00:10:01:01:02 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 101105 bytes 1829041
RX errors 0 dropped 18926930 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2057 bytes 926192
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
5.檢查ACI是否正在將資料包傳送出去,或者目的裝置是否正在接收資料包
在枝葉交換機的出口埠上進行SPAN捕獲,以便從故障排除路徑中消除ACI交換矩陣。
SPAN captures are carried out at the port of exit of the branch exchanger in order to remove the ACI switch matrix from the fault resolution path.
目的地上的Rx計數器也可用於從故障排除路徑中排除整個網路交換機,如前面的緩衝步驟所示。
The Rx counter on the destination can also be used to remove the entire network switch from the troubleshoot path, as shown by the buffer in the front.
本節介紹如何檢查端點擺動。可在以下檔案中找到更多詳情:
This section describes how to check peer swings. More details can be found in the following files:
當ACI在多個位置獲取同一MAC或IP地址時,終端似乎已移動。這也可能由欺騙裝置或配置錯誤導致。這種行為被稱為端點擺動。在這種情況下,流向移動/擺動端點的流量(橋接流量的MAC地址,路由流量的IP地址)將間歇性地失敗。
When ACI takes the same Mac or IP address at multiple locations, the end appears to have moved. This may also be caused by a fraud device or an error in configuration. This behaviour is called endpoint swinging. In this case, the flow to the moving/moved endpoint (the bridge-to-flow MAC address, the route-to-flow IP address) will fail intermittently.
檢測端點抖動的最有效方法是使用增強型端點跟蹤器。此應用可以作為ACI AppCenter應用運行,也可以在外部伺服器上作為獨立應用運行,以備需要管理更大的交換矩陣。
The most effective way to detect peer shaking is to use an enhanced peer tracker. This application can run as an ACI AppCenter application or as an independent application on an external server to prepare for the need to manage a larger switch matrix.
棄用警告!本指南寫於4.2;此後,Enhanced Endpoint Tracker應用已被棄用,取而代之的是Nexus儀表板見解上的功能。如需更多資訊,請參閱Cisco錯誤ID CSCvz59365  .
.
上圖顯示了AppCenter中的增強型終端跟蹤器。以下示例顯示如何使用增強型端點跟蹤器查詢擺動端點。
The above graph shows the enhanced end-tracker in AppCenter. The following examples show how to use the enhanced end-tracker to query the moving endpoint.
在本例中,IP 10.1.2.1應屬於具有MAC 0000.1001.0102的EP B。但是,具有MAC 0000.1001.9999的EP X也正在使用IP 10.1.2.1採購流量,原因是配置錯誤或可能是IP欺騙。
In this case, IP 10.1.2.1 should belong to EP B with MAC 0000.1001.0102. However, EP X with MAC 0000.1001.999 is also buying traffic using EP 10.1.2.1 because of a configuration error or possible IP fraud.
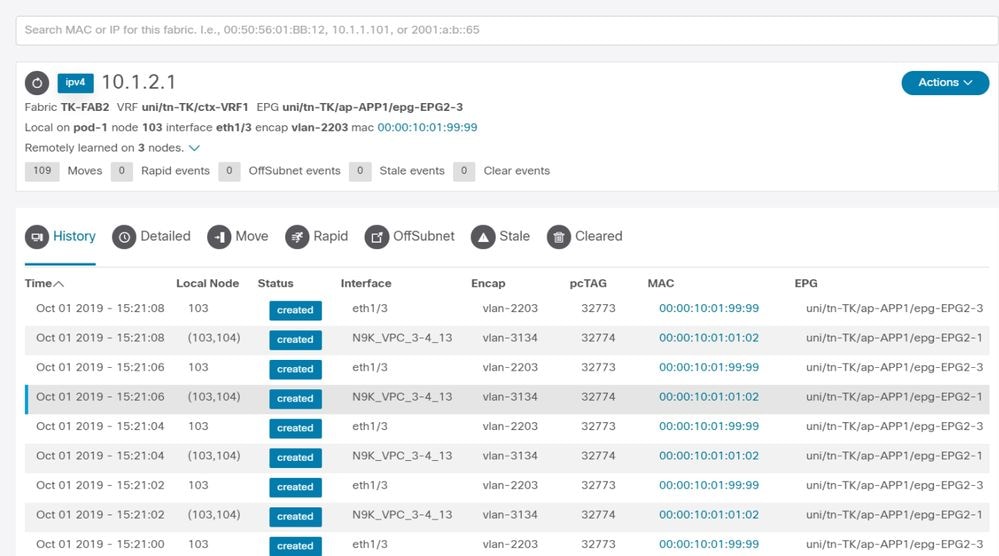
增強型終端跟蹤器顯示獲取IP 10.1.2.1的時間和位置。如上面的螢幕截圖所示,10.1.2.1正在使用MAC 0000.1001.0102(預期)和0000.1001.9999(預期)在兩個端點之間擺動。 這將導致發往IP 10.1.2.1的可達性問題,因為當在錯誤的MAC地址上獲知資料包時,將通過錯誤的介面將其傳送到錯誤的裝置。要解決此問題,請採取措施防止意外的VM使用不合適的IP地址查詢流量。
An enhanced end-tracker displays the time and location of access to IP 10.1.2.1, as shown in the screenshot above, is moving between the two endpoints using MAC10.1001.0102 (expected) and 0.000.1001.9999 (expected). This will lead to a passability problem to IP 10.1.2.1, because when the information package is available on the wrong MAC address, it will be passed to the wrong device via the wrong interface. To solve this problem, take measures to prevent unexpected VM from using an inappropriate IP address to query traffic.
下面顯示了由於配置不當導致的終端擺動的典型示例。
The following is a typical example of end-of-life swings due to misconfiguration.
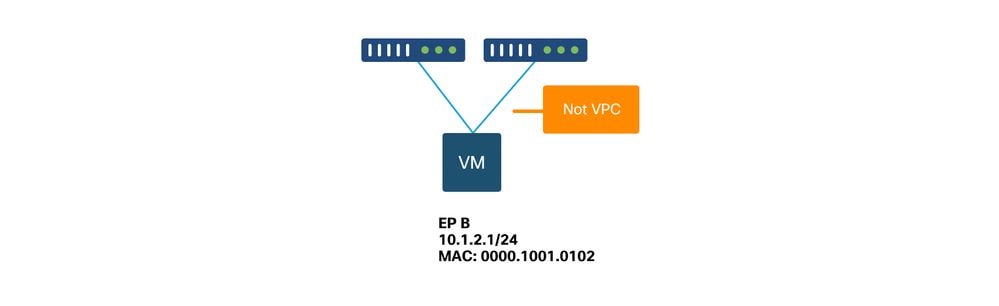
當伺服器或VM通過兩個沒有VPC的介面連線到ACI枝葉節點時,伺服器需要使用主用/備用網絡卡分組。否則,封包會被負載均衡到兩個上行鏈路,且從ACI枝葉交換器的角度來看,端點看起來好像在兩個介面之間擺動。在這種情況下,需要主用/備用或等效的NIC組合模式,或者僅使用ACI端的VPC。
When the server or VM goes through two non-VPC interfaces to the ACI branch node, the server needs to use the main/back-up network card component. Otherwise, the package will be load-balanced to the top two links and, from the ACI branch exchanger point of view, the endpoint appears to be moving between the two interfaces. In this case, the main/back-up or equivalent NIC combination mode is required, or only the ACI-end VPC.
本章介紹如何檢查與輸入介面捨棄相關的主要計數器。
This chapter describes how to check the main calculator associated with the input interface's abandonment.
在以ACI模式運行的Nexus 9000交換機上,ACI上有三個主要硬體計數器用於入口介面丟棄。
On the Nexus 9000 switchboard operated in the ACI mode, three major hardware calculators were discarded by the ACI interface.
轉發
下降的主要原因包括:
The main reasons for this decline include:
- SECURITY_GROUP_DENY:由於缺少允許通訊的合約而丟棄此項。
- VLAN_XLATE_MISS:由於VLAN不當而丟棄的。例如,幀進入具有802.1Q VLAN 10的交換矩陣。如果交換機在埠上具有VLAN 10,它將檢查內容並根據目標MAC做出轉發決策。但是,如果該連線埠上不允許VLAN 10,則會捨棄該連線埠,並將其標籤為VLAN_XLATE_MISS。
- ACL_DROP:由於SUP-TCAM而下降。ACI交換機中的SUP-TCAM包含要在正常L2/L3轉發決策之上應用的特殊規則。SUP-TCAM中的規則是內建的,不可由使用者配置。SUP-TCAM規則的主要目的是處理某些異常或某些控制平面流量,而不是由使用者檢查或監控。當封包符合SUP-TCAM規則且規則為捨棄封包時,捨棄的封包會計為ACL_DROP,且會增加轉送捨棄計數器。
轉發丟棄實質上是指由於有效已知原因而丟棄的資料包。它們通常可以忽略,不會導致效能下降,這與實際資料流量丟棄不同。
Re-disposal refers to information packages that are discarded for valid known reasons. They are often ignored and do not lead to reduced efficiency, which is different from actual data traffic.
錯誤
當交換機收到無效幀時,該幀會作為錯誤被丟棄。示例包括具有FCS或CRC錯誤的幀。有關詳細資訊,請參見後面的「CRC — FCS — 直通交換」一節。
Examples include those with FCS or CRC errors. For more details, please refer to the section on "CRC-FCS-Direct Exchange" at the end.
緩衝區
當交換器收到訊框時,如果沒有緩衝區可用於輸入或輸出,該訊框將以「Buffer」標籤。 這通常提示網路中的某個位置存在擁塞。表示錯誤的連結可能已滿,或包含目的地的連結已擁塞。
When the switcher receives the message box, if there is no buffer area available for input or output, the message box will be marked with the 'Buffer' label. This usually suggests that there is a plug in a location in the network. The wrong link may be full, or the link containing the destination is blocked.
使用API收集計數器
值得注意的是,通過使用API和對象模型,使用者可以快速查詢交換矩陣中這些丟包的所有例項(從apic運行這些例項)。
It is worth noting that, by using API and match models, users can quickly query all cases of these lost packages in the switch matrix (which run from apic). & nbsp;
# FCS Errors (non-stomped CRC errors)
moquery -c rmonDot3Stats -f 'rmon.Dot3Stats.fCSErrors>="1"' | egrep "dn|fCSErrors"
# FCS + Stomped CRC Errors
moquery -c rmonEtherStats -f 'rmon.EtherStats.cRCAlignErrors>="1"' | egrep "dn|cRCAlignErrors"
# Output Buffer Drops
moquery -c rmonEgrCounters -f 'rmon.EgrCounters.bufferdroppkts>="1"' | egrep "dn|bufferdroppkts"
# Output Errors
moquery -c rmonIfOut -f 'rmon.IfOut.errors>="1"' | egrep "dn|errors"
如果發現故障,或者需要使用CLI檢查介面上的丟包情況,最好的方法是檢視硬體中的平台計數器。並非所有計數器都使用「show interface」顯示。 三個主要捨棄原因只能使用平台計數器檢視。要檢視這些資訊,請執行以下步驟:
If a fault is detected, or if CLI is needed to check the drop on the interface, the best way to do this is to look at the platform calculators in the hardware. Not all of the calculators are shown using "show interface". The three main causes of abandonment can only be viewed using the platform calculator. To view the information, do the following steps:
葉
通過SSH連線到枝葉並運行這些命令。以下範例適用於ethernet 1/31。
Runs these commands via SSH links to the branch. The following example is appropriate for each othernet 1/31.
ACI-LEAF# vsh_lc
module-1# show platform internal counters port 31
Stats for port 31
(note: forward drops includes sup redirected packets too)
IF LPort Input Output
Packets Bytes Packets Bytes
eth-1/31 31 Total 400719 286628225 2302918 463380330
Unicast 306610 269471065 453831 40294786
Multicast 0 0 1849091 423087288
Flood 56783 8427482 0 0
Total Drops 37327 0
Buffer 0 0
Error 0 0
Forward 37327
LB 0
AFD RED 0
...
骨幹
可以使用與枝葉交換機相同的方法檢查固定主幹(N9K-C9332C和N9K-C9364C)。
A fixed backbone (N9K-C9332C and N9K-C9364C) can be checked using the same method as a branch exchanger.
對於模組化主幹(N9K-C9504等),必須先將線卡連線到才能檢視平台計數器。使用SSH連線到脊柱並運行這些命令。以下範例適用於ethernet 2/1。
For modular backbones (N9K-C9504 et cetera), a line card must be connected to the platform counter before it can be viewed. Use the SSH link to the spine and run these commands. The following example is appropriate for each othernet 2/1.
ACI-SPINE# vsh
ACI-SPINE# attach module 2
module-2# show platform internal counters port 1
Stats for port 1
(note: forward drops include sup redirected packets too)
IF LPort Input Output
Packets Bytes Packets Bytes
eth-2/1 1 Total 85632884 32811563575 126611414 25868913406
Unicast 81449096 32273734109 104024872 23037696345
Multicast 3759719 487617769 22586542 2831217061
Flood 0 0 0 0
Total Drops 0 0
Buffer 0 0
Error 0 0
Forward 0
LB 0
AFD RED 0
...
使用「show queuing interface」顯示排隊統計資訊計數器。 以下範例適用於ethernet 1/5。
The example below is suitable for the restnet 1/5.
ACI-LEAF# show queuing interface ethernet 1/5
================================================================================
Queuing stats for ethernet 1/5
================================================================================
================================================================================
Qos Class level1
================================================================================
Rx Admit Pkts : 0 Tx Admit Pkts : 0
Rx Admit Bytes: 0 Tx Admit Bytes: 0
Rx Drop Pkts : 0 Tx Drop Pkts : 0
Rx Drop Bytes : 0 Tx Drop Bytes : 0
================================================================================
Qos Class level2
================================================================================
Rx Admit Pkts : 0 Tx Admit Pkts : 0
Rx Admit Bytes: 0 Tx Admit Bytes: 0
Rx Drop Pkts : 0 Tx Drop Pkts : 0
Rx Drop Bytes : 0 Tx Drop Bytes : 0
================================================================================
Qos Class level3
================================================================================
Rx Admit Pkts : 1756121 Tx Admit Pkts : 904909
Rx Admit Bytes: 186146554 Tx Admit Bytes: 80417455
Rx Drop Pkts : 0 Tx Drop Pkts : 22
Rx Drop Bytes : 0 Tx Drop Bytes : 3776
...
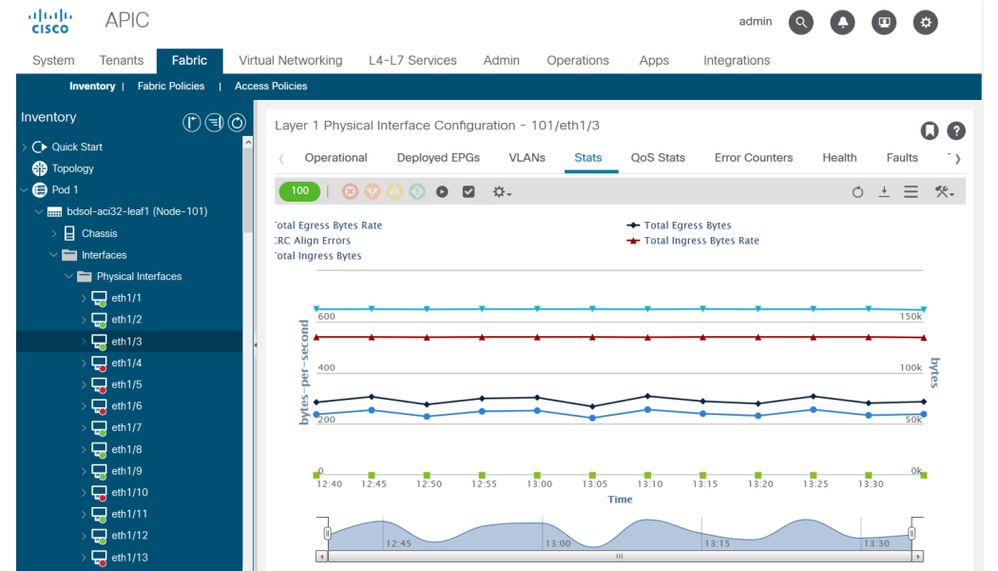
位置是「交換矩陣>清單>枝葉/骨幹>物理介面>統計資訊」。
The position is "exchange matrix & gt; list & gt; branch/brain & gt; physical interface & gt; statistical information".
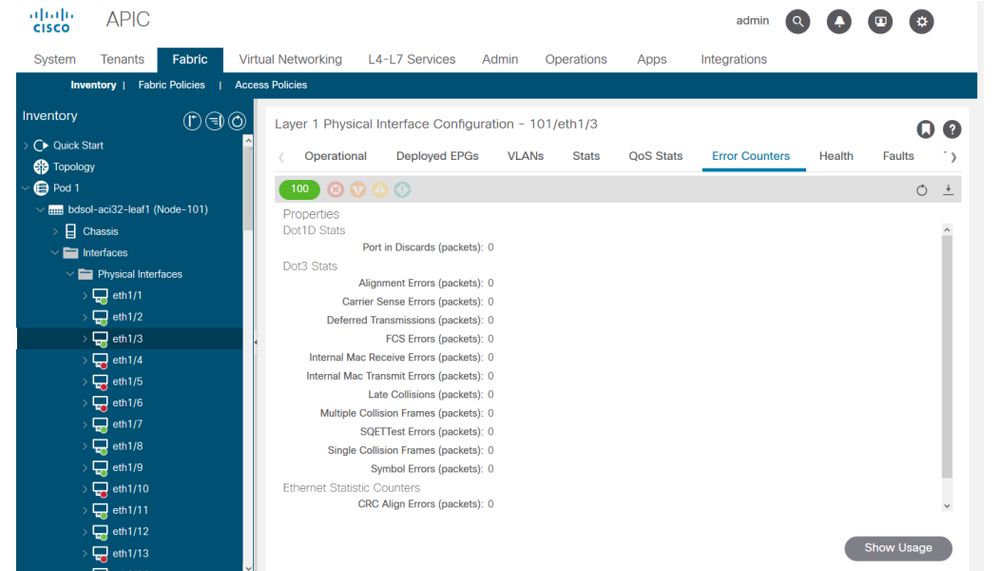
錯誤統計資訊可在同一位置看到:
Error statistics can be seen at the same location:
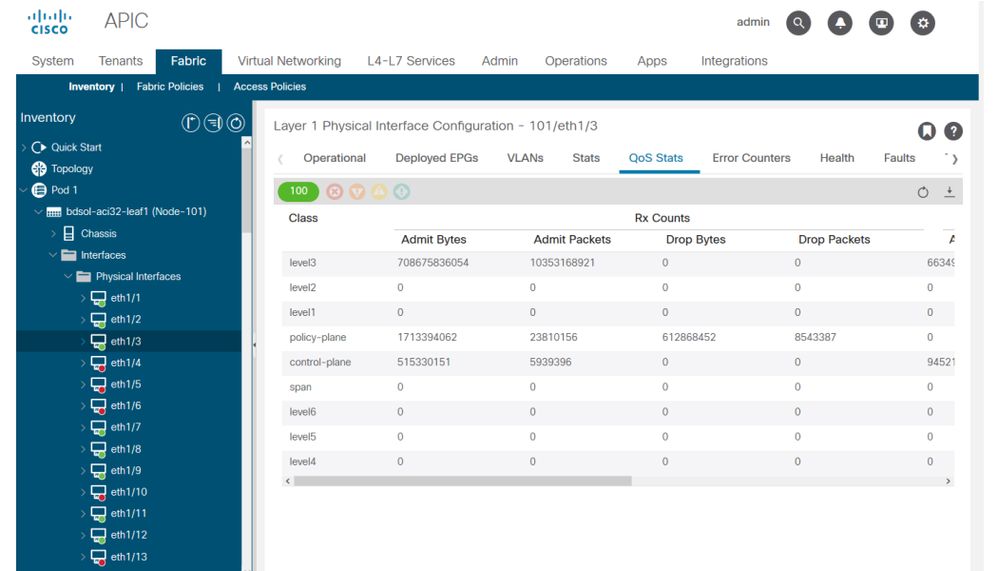
最後,GUI可以顯示每個介面的QoS統計資訊:
Finally, GUI can show QoS statistics for each interface:
什麼是循環冗餘檢查(CRC)?
CRC是幀上的多項式函式,它在乙太網中返回4B數字。它將捕獲所有單位元錯誤和相當比例的雙位元錯誤。因此,其目的是確保幀在傳輸過程中未損壞。如果CRC錯誤計數器增加,這意味著當硬體在幀上運行多項式函式時,結果為4B數,與幀本身上發現的4B數不同。幀可能會由於多種原因而損壞,例如雙工不匹配、佈線故障和硬體損壞。但是,應該會遇到一定程度的CRC錯誤,該標準允許乙太網上的最高10-12位錯誤率(1012中的1位可以反轉)。
CRC is a multi-function function, which returns 4B numbers on the Aethernet. It captures all unit errors and proportional double-bit errors. The aim is therefore to ensure that the platinum remains intact in the transmission process. If the CRC error calculator increases, this means that when the hard body runs multiple functions on the platinum, the result is 4B, which is different from the 4B found on the platinum itself.
儲存轉發與直通交換
儲存轉發和直通第2層交換機都根據資料包的目的MAC地址做出轉發決策。當站點與網路上的其他節點通訊時,它們檢查資料包的源MAC(SMAC)欄位時也會學習MAC地址。
You can also learn the MAC address when you check the source MAC (SMAC) column of the package.
儲存轉發交換機在收到整個幀並檢查其完整性之後,會對資料包做出轉發決定。直通交換機檢查傳入幀的目標MAC(DMAC)地址後不久就開始執行轉發過程。但是,直通交換機必須等待檢視完整個資料包,才能執行CRC檢查。這表示在驗證CRC時,資料包已經轉發,如果檢查失敗,則無法丟棄。
After receiving the entire package and checking its integrity, a decision is made to transfer the package. The switchboard checkes the target MAC (DMAC) address that was sent to the switchboard shortly after the transfer. However, the switcher must wait to see the complete package before executing the CRC check. This means that the package was forwarded at the time of the verification of the CRC, and if the check failed, it could not be discarded.
傳統上,大多數網路裝置都是基於儲存轉發來運行的。直通交換技術往往用於要求低延遲轉發的高速網路。
Traditionally, most network devices operate on the basis of storage and transmission.
具體而言,對於第2代和更高版本的ACI硬體,如果輸入介面速度較高,而輸出介面速度相同或較低,則執行直通交換。如果輸入介面速度低於輸出介面,則會完成儲存和轉送交換。
Specifically, for ACI versions of the 2nd generation and higher, if the input interface is higher and the output interface is the same or lower, the direct traffic switch is performed. If the input interface is lower than the output interface, the storage and transfer are completed.
踩踏
具有CRC錯誤的資料包需要丟棄。如果在直通路徑中交換幀,則在轉發資料包後會進行CRC驗證。因此,唯一的選項是停止乙太網幀校驗序列(FCS)。停止幀涉及將FCS設定為不通過CRC校驗的已知值。因此,一個未通過CRC的壞幀會在它經過的每個介面上顯示為CRC,直到它到達將丟棄它的儲存轉發交換機。
The files with the CRC error need to be discarded. If they are exchanged in a straight-through path, they will be verified by the CRC. The only option is therefore to stop the Ethernet calibration sequence (FCS). The stoppage involves setting the FCS to a known value that will not be tested by the CRC. Thus, a bad box that has not passed the CRC will be shown as CRC in every channel through which it passes until it reaches the storage switch that will discard it.
ACI和CRC:查詢有故障的介面
- 如果枝葉在下行鏈路埠上看到CRC錯誤,則主要問題是下行鏈路SFP或外部裝置/網路上的元件問題。
- 如果脊柱看到CRC錯誤,則主要是在本地埠、SFP、光纖或鄰居SFP上出現問題。來自枝葉下行鏈路的CRC故障資料包不會儲存到主幹。如同其報頭可讀一樣,其是VXLAN封裝並將計算新的CRC。如果報頭因幀損壞而無法讀取,資料包將被丟棄。
- 如果枝葉在交換矩陣鏈路上看到CRC錯誤,則可能是:
- 本地光纖/SFP對、主幹的輸入光纖或SFP對出現問題。
- 一個從布料中穿過的窄邊框。
踩踏:跳轉故障排除
- 查詢交換矩陣上存在FCS錯誤的介面。由於FCS發生在埠本地,因此很可能是光纖或SFP位於任一端。
- 「show interface」輸出上的CRC錯誤反映了總的FCS+Stomp值。\
舉個例子:
Let me give you an example:
使用指令檢查連線埠
Check ports with command
vsh_lc: 'show platform internal counter port <X>'
在此命令中,3個值非常重要:
In this order, three values are important:
- RX_FCS_ERR - FCS故障。
- RX_CRCERR — 收到堆疊的CRC錯誤幀。
- TX_FRM_ERROR — 傳輸的CRC錯誤幀。
module-1# show platform internal counters port 1 | egrep ERR
RX_FCS_ERR 0 ---- Real error local between the devices and its direct neighbor
RX_CRCERR 0 ---- Stomped frame --- so likely stomped by underlying devices and generated further down the network
TX_FRM_ERROR 0 ---- Packet received from another interface that was stomp on Tx direction
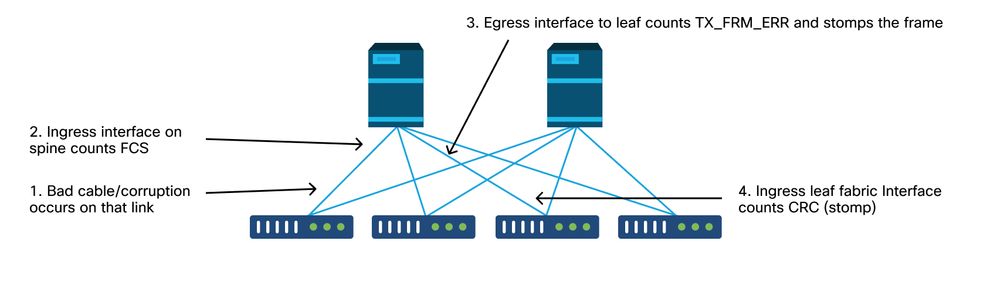
如果損壞的鏈路生成大量損壞的幀,則這些幀可能會泛洪到所有其他枝葉節點,並且很容易在交換矩陣中大多數枝葉節點的交換矩陣上行鏈路入口上找到CRC。這些可能都來自一個損壞的鏈路。
If the broken links generate a large number of damaged thugs, they may flood to all other branch nodes and easily find the CRC at the entrance to the switch nodes of most of the swap matrix. These may all come from a broken link.
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群
















发表评论