.当今,随着互联网技术的迅速发展,采用以太网实现数据采集和控制方面的应用,成为了电子系统设计的热点。以太网具有价格低廉、稳定可靠、传输速度快、传输距离远等特点,以太网技术发展成熟,具有很高的性价比。采用以太网技术的设备,可以通过TCP/IP协议进行数据的传输,不需要进行传输协议转换,使用和维护设备简单。随着技术的发展和各类应用的需求,出现了各种以太网的标准,包括标准以太网(10Mbit/s)、百兆以太网(100Mbit/s)、千兆以太网(1000Mbit/s)和10G(10Gbit/s)以太网。不同类型的以太网有其各自需要遵循的标准,同时其所用的传输介质以及数据吞吐量也各不相同。
Today, with the rapid development of Internet technology, the use of to achieve data collection and control applications have become electronic system design hotspots with low cost, reliability, speed of transmission, distance of transmission, etc., matured in ultranet technology, with high cost. Equipment using electronics electronics, with the need for various applications. Various standards have emerged in the web, including standards for toonet (10Mibit/s), 100 megagrams of technology (100 kilos) and
千兆以太网技术作为新一代的高速以太网技术,它可以提供1Gbps的通信带宽,采用和传统10M、100M以太网同样的CSMA/CD协议、帧格式和帧长、全/半双工工作方式、流控模式以及布线系统,给用户带来了提高核心网络的有效解决方案,这种解决方案的最大优点是继承了传统以太网技术价格便宜的特点。 A Gbps network, whose greatest advantage is to inherit the traditional toonet technology cheapness.
对于学习者而言,你就是要搞清楚弄明白以太网如何去实现,在实际操作中怎么去做,从这个角度出发的话,你就会发现其实没那么复杂,这就是说起来没那么难。那真正实现起来,到具体的各个接口以及细节的调试以及调通,你会发现还是比较烧脑的。所以呢,咱们先来聊一聊以太网的各个接口,从大体框架来分析如何去学习。 For a learner, you're trying to figure out how the Ethernet works, how it works in practice, and from this point of view, it's not really that complicated, which is to say it's not that hard. That really works, to the specific //a> and how the details are calibrated and tuned. So let's talk about the interfaces of the Ethernet and analyze how to learn from the general framework.
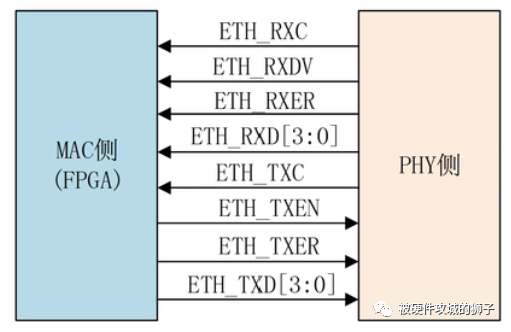
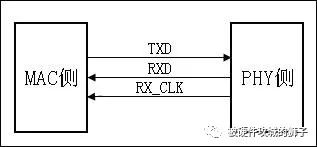
先说百兆网,百兆网的接口一般为MII(Media Independent Interface),当然10M网用的也是MII接口。 begins with the 100-meganet , where the interface is generally MediaIndependent Interface and, of course, the 10M network also uses the MII interface.
在百兆网模式下,其RXCLK的周期为40ns,也就是25M,数据端口RXD只用了4根线RXD[3:0],然后25M*4=100M,这样算出来,就是100M的速率了。 In meganet mode, RXCLK has a 40n, or 25M, data
MII接口
通信速率10M/100M(百兆以太网的通信接口) Communications rate of 10M/100M (@a href="https://m.elecfans.com/v/tag/13179/"target="_blank" communications interface)
ETH_RXC:PHY侧输出给MAC的以太网的接受时钟 ETH_RXC: The acceptance of the Ethernet exported to MAC side by PHY clock
ETH_RXDV:PHY侧输出给MAC的接收有效信号 ETH_RXDV: PHY side output to MAC is valid for reception
ETH_RXER:PHY侧输出给MAC的接收错误信号 ETH_RXER: PHY side output to MAC error signal
ETH_RXD:PHY侧输出给MAC的4位接收数据 ETH_RXD: PHY side output to MAC 4 bits to receive data
只有当ETH_RXDV为高电平,ETH_RXER为低电平时,这时传输的数据才是有效数据 Only when ETH_RXDV is high and ETH_RXER is low is the data transmitted is valid
ETH_TXC:发射时钟同样是有PHY芯片提供给MAC的 ETH_TXC: Launch clock is also PHY chip for MAC
ETH_TXEN:MAC提供给PHY芯片的发送使能信号 ETH_TXEN: MAC sending energy signal for PHYs chip
ETH_TXER:MAC提供给PHY芯片的发送错误指示信号 ETH_TXER: Misdirection signal given by MAC to PHY chip
ETH_TXD:MAC提供给PHY芯片的待发送的4位数据 ETH_TXD: MAC to send 4-bit data for PHY chip
只有当ETH_TXEN为高电平,ETH_TXER为低电平时,这时传输的数据才是有效数据 The data transmitted is valid only when ETH_TXEN is high and ETH_TXER is low.
10M:时钟为2.5MHz,单沿采样;100M:时钟为25MHz,单沿采样 10M: 2.5 MHz clock, single sample; 100M: 25 MHz clock, single sample
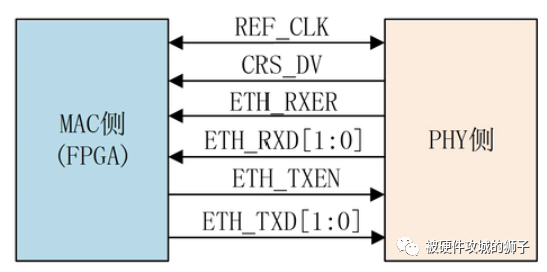
RMII接口(Reduced MII)
通信速率为10M/100M Communication rate at 10M/100M
发送数据核接收数据都是两位的; (a) Sending data for nuclear reception data on both sides;
参考时钟通常是由外部晶振提供给MAC侧或PHY芯片的; Reference clocks are usually provided to MAC side or PHY chip by external crystallization;
CRS和DV信号复用一个端口; C RS/a> and DV signals revert to one port;
10M:时钟为5M,单沿采样;100M:时钟为50M,单沿采样 10M: 5M clock, single sample; 100M: 50M clock, single sample
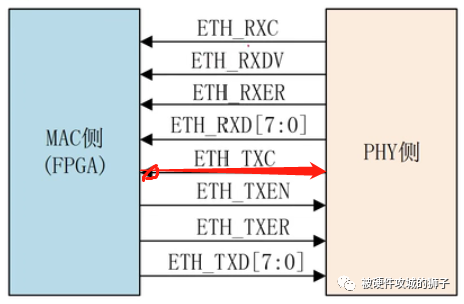
接着再来说一下千兆网,千兆网的接口,就目前接触比较多的接口有3种,GMII,RGMII和SGMII。 goes on to say a few words about the Giganet , the Giganet interface, which currently has three more interfaces, GMII, RGMII and SGMII.
先说GMII,RxClk的周期为8ns,也就是125M,数据端口使用了8bit,125M*8=1000M,速率就是千兆网了。 begins with GMII, RxClk has a cycle of 8ns, or 125M, and the data portal uses 8bit, 125M*8=1000M, with a Giganet rate.
通信速率1G/100M/10M Communication rate 1G/100M/10M
与MII接口相比,TXC由MAC侧产生(原图中画错了),并且将数据位宽从4位提高到了8位; TXC is generated from the MAC side (the original picture was wrong) compared to the MII interface and has increased the size of the data from 4 to 8 places;
10M:时钟为2.5M,单沿采样,只用到了4位;100M:时钟为25M,单沿采样,只用到了4位;1G:时钟为125M,单沿采样 10M: 2.5M clock, only 4 places for single sampling; 100M: 25M clock, only 4 places for single sampling; 1G: 125M clock, only for single sampling
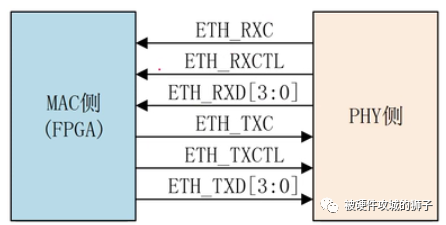
还有RGMII,其时钟频率也为125M,但是它只使用了4个线,不过,RGMII使用的是双沿模式,也就是DDR模式,在时钟的上下沿都可以传送数据。这样算的话,125M*4*2=1000M,还是千兆网。RGMII与GMII主要的区别就是双沿采样与单沿采样。
通信速率为1G/100M/10M Communication rate at 1G/100M/10M
TXC由MAC侧产生; TXC is generated from the MAC side;
将RXDV和RXER信号集成到了RXCTL上,时钟上升沿采到的是RXDV,下降沿采到的是RXDV^RXER(异或); The RXDV and RXER signals are integrated into RXCTL and the clock rises along RXDV and the fall along RXDVRXER (similar or different);
将TXEN和TXER信号集成到了TXCTL上,时钟上升沿采到的是TXEN,下降沿采到的是TXEN^TXER(异或); The TXEN and TXER signals are integrated into TXCTL, where the clock rises along with TXEN and drops along with TXENTXER (similar or different);
数据位宽由8位减少到了4位; The data width was reduced from 8 to 4 places;
1G:时钟为125M,双沿采样;100M:时钟为25M,单沿采样;10M:时钟为2.5M,单沿采样 1G: 125M clock, double sample; 100M: 25M clock, single sample; 10M: 2.5M clock, single sample
之后还有SGMII,全称为Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface,也就是串行的以太网接口。MII,GMII还是RGMII,都是使用并行接口,而且还需要随路时钟,而SGMII只需要2组线,一组是发送,一组是接收,当然一组线由两根差分线组成。SGMII_TXP/N,SGMII_RXP/N;SGMII也是需要8/10B编码。这样在PCB布线时,就可以节省一些布线的空间。
审核编辑:刘清
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群















发表评论